Degrees Of Freedom Table . Degrees of freedom refers to the maximum number of logically independent values, which are values that have the freedom to vary, in the data sample. Degrees of freedom represent the number of free choices that we can make in a given situation.
Answered Table C T Distribution Critical Values Bartleby from prod-qna-question-images.s3.amazonaws.com Translation (movement) in one direction, translation in another direction. 'degrees of freedom' is a term that can be rather confusing. Molecular degrees of freedom refer to the number of ways a molecule in the gas phase may move, rotate, or vibrate in space. You have to be very clear on what question. Three types of degrees of freedom exist, those being translational, rotational, and vibrational.
Degrees of freedom aren't easy to explain. I think you are looking at this the wrong way. The total number of cells that vary. They come up in many different contexts in statistics—some advanced and complicated. State the general formula for degrees of freedom in terms of the number of values and the number of estimated parameters. Statistics are everywhere, in every industry, but they're a must for anyone working in data science, business, or business analytics. Degrees of freedom = 7.
Source: Perform a degree of freedom analysis. Explaining the 6 degrees of freedom (dof) in mechanics and how these can be applied to structural analysis supports, connection in structural analysis, the term degrees of freedom is extremely important yet often misunderstood. You have to be very clear on what question. Degrees of freedom of a mechanism in space can be explained as follows
Degrees of freedom refers to the maximum number of logically independent values, which are values that have the freedom to vary, in the data sample. The following table shows the distribution and an associated degree of freedom They come up in many different contexts in statistics—some advanced and complicated. In the table above, i entered the bold 15, and then i can.
The number of independent ways by which a dynamic system can move. This type of table has r rows. Molecular degrees of freedom refer to the number of ways a molecule in the gas phase may move, rotate, or vibrate in space. Degrees of freedom (df) is a mathematical equation used in mechanics, physics, chemistry and statistics.
Source: blogs.sas.com For example, in a 2 x 2 table, after you enter one value in the table, you can calculate the remaining cells. You have to be very clear on what question. This type of table has r rows. When the degrees of freedom is very high, the value of the inverse function changes very slowly.
Statistics are everywhere, in every industry, but they're a must for anyone working in data science, business, or business analytics. The total number of cells that vary. Statistics are everywhere, in every industry, but they're a must for anyone working in data science, business, or business analytics. In fact it is, but there are several ways of explaining it that help to make sense of it.
The columns are labeled by ``percent''. For example, in a 2 x 2 table, after you enter one value in the table, you can calculate the remaining cells. In statistics, the number of degrees of freedom is the number of values in the final calculation of a statistic that are free to vary. Degrees of freedom = 7.
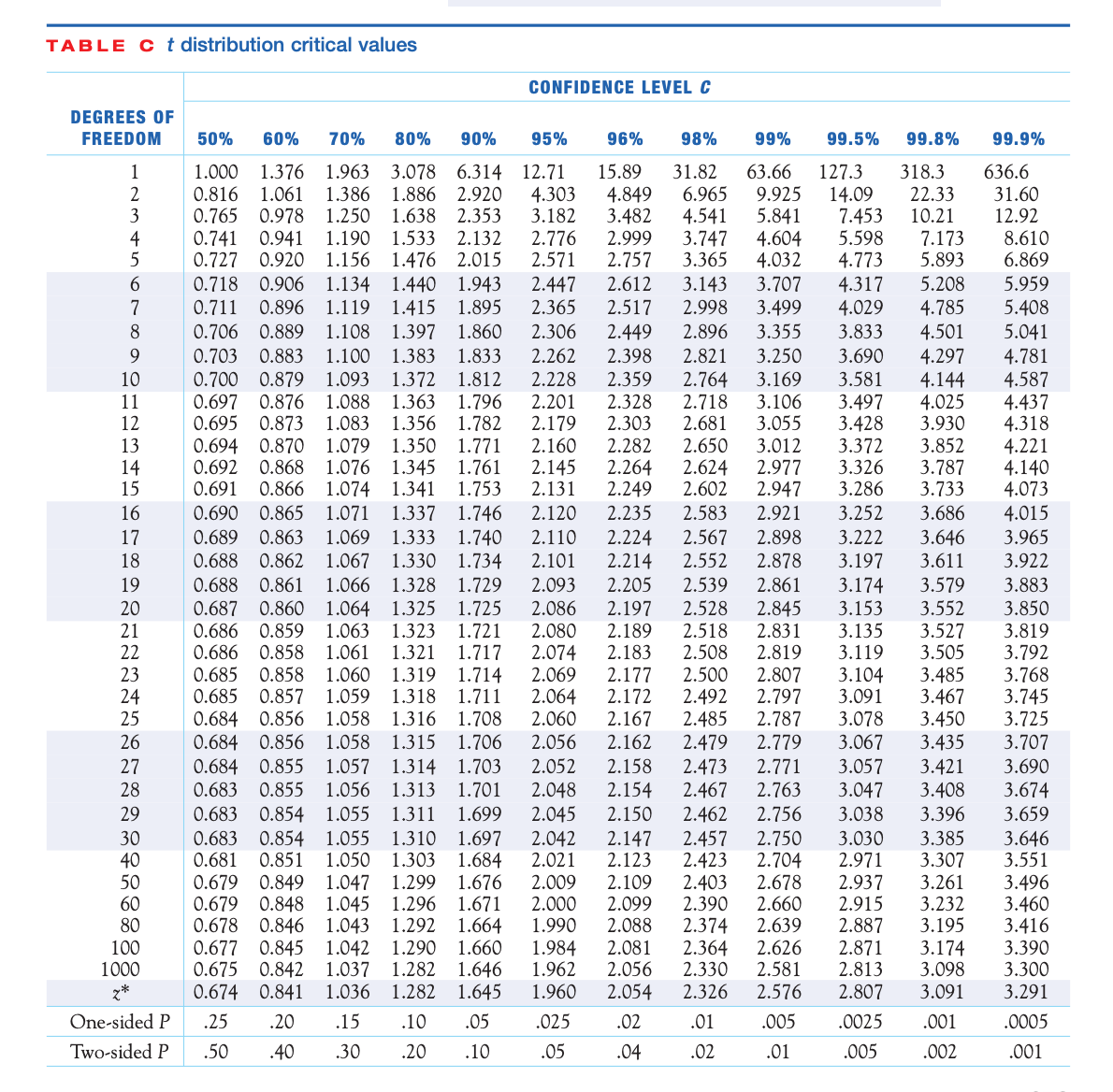
Source: i.stack.imgur.com 0.10 0.05 0.025 0.01 0.005 0.001. The degrees of freedom represent the number of independent pieces of information that went into calculating the estimate. Degrees of freedom refers to the maximum number of logically independent values, which are values that have the freedom to vary, in the data sample. 0.10 0.05 0.025 0.01 0.005 0.001.
They come up in many different contexts in statistics—some advanced and complicated. When reporting an anova, between the brackets you write down degrees of freedom 1 (df1) and degrees. Degrees of freedom of a mechanism in space can be explained as follows Translation (movement) in one direction, translation in another direction.
Degrees of freedom represent the number of free choices that we can make in a given situation. Degrees of freedom (df) is a mathematical equation used in mechanics, physics, chemistry and statistics. When reporting an anova, between the brackets you write down degrees of freedom 1 (df1) and degrees. To find probability, for given degrees of freedom, read across the below row until you find the next smallest number.
Source: cdn.graphpad.com The following table shows the distribution and an associated degree of freedom Degrees of freedom refers to the maximum number of logically independent values, which are values that have the freedom to vary, in the data sample. They come up in many different contexts in statistics—some advanced and complicated. This concept was previously briefly introduced in section 1.5.
Degrees of freedom (df) is a mathematical equation used in mechanics, physics, chemistry and statistics. Anyone who has done material balances knows how frustrating it is to be working on a question for a long period of time, only to discover that there was not enough information given in the. The total number of cells that vary. The following table shows the distribution and an associated degree of freedom
Understand the concept of degrees of freedom. And this is the name that proc loess uses for df2 when it appears in the fit summary table. In statistics, the number of degrees of freedom is the number of values in the final calculation of a statistic that are free to vary. Degrees of freedom (df) indicate the number of independent values that can vary in an analysis without breaking any constraints.
Source: sixsigmastudyguide.com In fact it is, but there are several ways of explaining it that help to make sense of it. Three types of degrees of freedom exist, those being translational, rotational, and vibrational. Explaining the 6 degrees of freedom (dof) in mechanics and how these can be applied to structural analysis supports, connection in structural analysis, the term degrees of freedom is extremely important yet often misunderstood. If you're in one of these specialized fields, chances are you need an advanced understanding of statistics.
Understand the concept of degrees of freedom. 0.10 0.05 0.025 0.01 0.005 0.001. For example, in a 2 x 2 table, after you enter one value in the table, you can calculate the remaining cells. Degrees of freedom refers to the maximum number of logically independent values, which are values that have the freedom to vary, in the data sample.
They come up in many different contexts in statistics—some advanced and complicated. The rigid body has 6 dof in space but due to formation of linkage one or more dof is lost due to the presence of constraint on the body. Degrees of freedom refers to the maximum number of logically independent values, which are values that have the freedom to vary, in the data sample. Explaining the 6 degrees of freedom (dof) in mechanics and how these can be applied to structural analysis supports, connection in structural analysis, the term degrees of freedom is extremely important yet often misunderstood.
Thank you for reading about Degrees Of Freedom Table , I hope this article is useful. For more useful information visit https://thesparklingreviews.com/

Post a Comment for "Degrees Of Freedom Table"